For chronic weight management as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with body weight greater than 60 kg and obesity, and for adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight related comorbid condition. Click for Limitations of Use.
Adverse Events
Safety and Tolerability of Saxenda® Were Evaluated in 5 Clinical Studies1
Adverse reactions, in studies up to 56 weeks, reported in ≥2% of patients treated with Saxenda® and more frequently than with placebo1
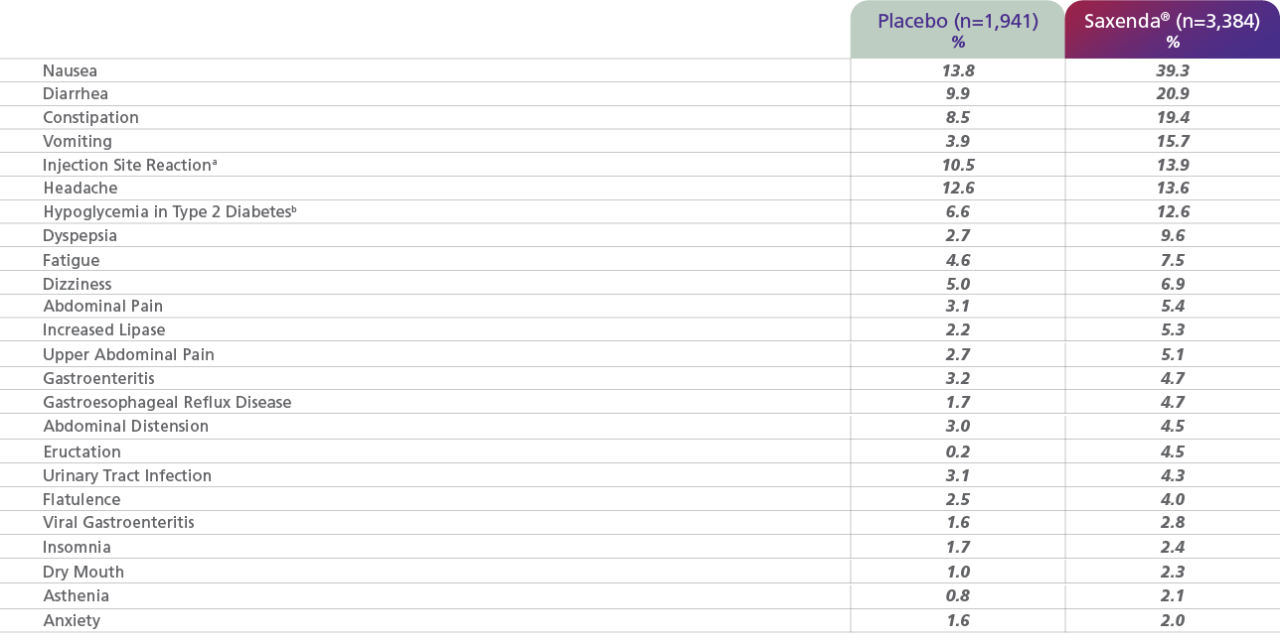
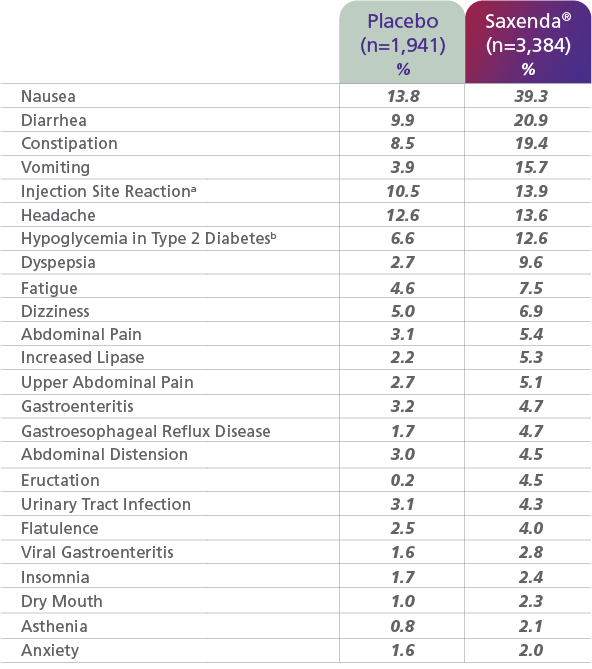
aThe most common reactions, each reported by 1% to 2.5% of Saxenda®-treated patients and more commonly than by placebo-treated patients, included erythema, pruritus, and rash at the injection site.
bDefined as blood glucose <54 mg/dL with or without symptoms of hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes not taking concomitant insulin (Study 2, Saxenda® n=423, Placebo n=212).

In a 3-year study, the safety profile of Saxenda® was consistent with previous 56-week studies2
Discontinuation Rates
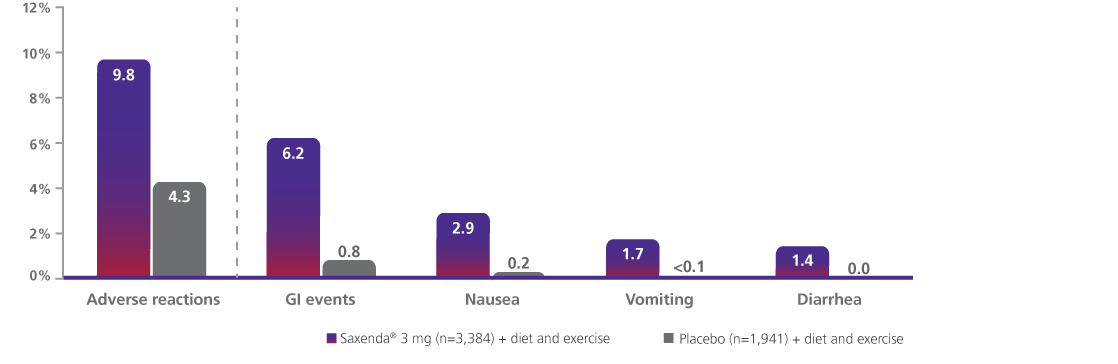
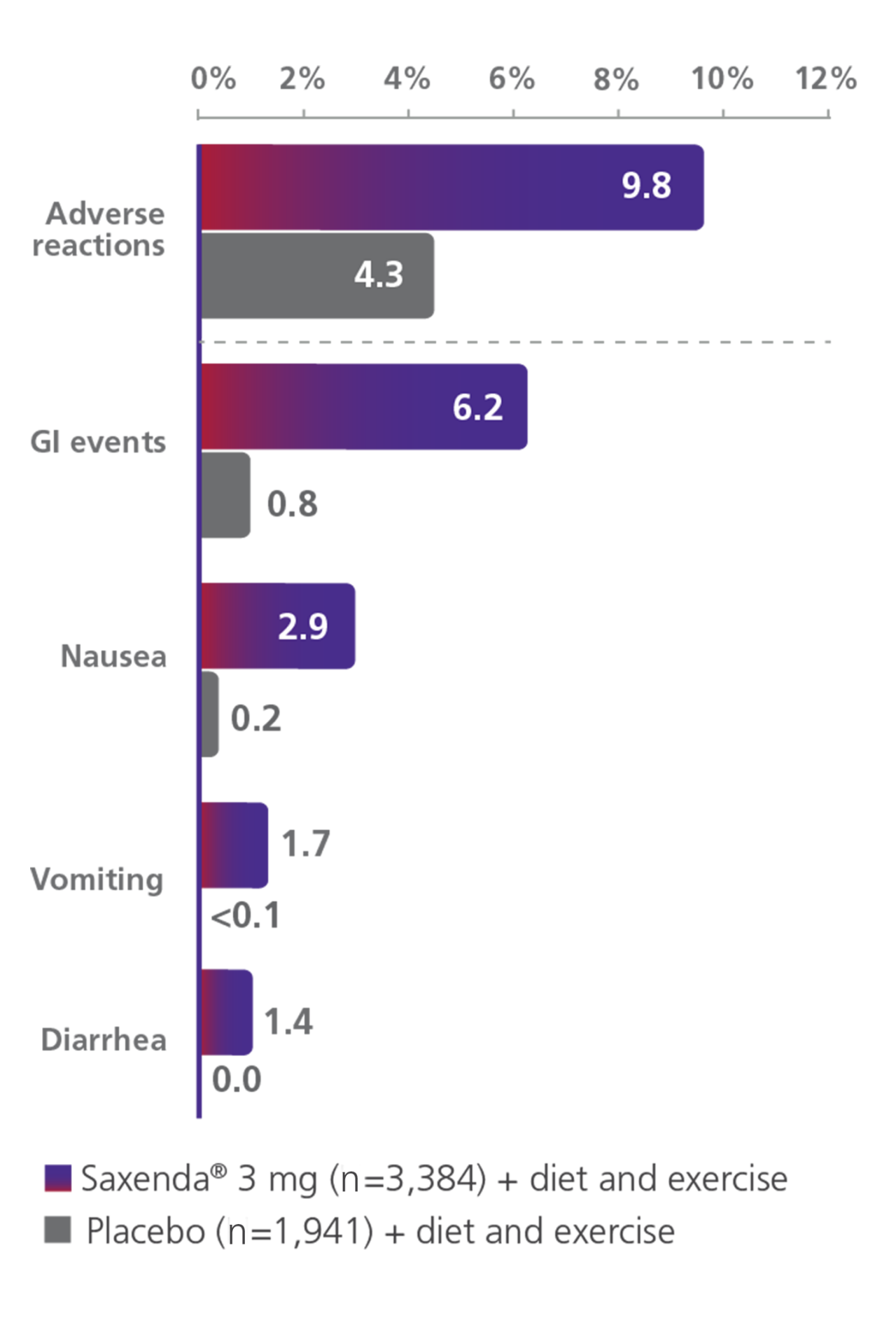
Discontinuation due to adverse events was evaluated in 5 clinical trials1
- In the clinical trials, approximately 68% of patients taking Saxenda® and 39% of patients on placebo reported GI disorders; the most frequently reported was nausea (39% and 14% of patients treated with Saxenda® and placebo, respectively)1
- Most episodes of GI events were mild or moderate and did not lead to discontinuation of therapy (6.2% with Saxenda® vs 0.8% with placebo discontinued treatment as a result of GI adverse reactions)1
Discontinuation due to adverse reactions1
Study 1 (1 year)1,3
- Results from a 56-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Saxenda®
- Adult patients with a BMI of ≥30, or ≥27 with 1 or more weight-related comorbidities (n=3,731) were randomized to receive once-daily Saxenda® (n=2,487) or placebo (n=1,244) in conjunction with a lifestyle modification program that included increased physical activity and a 500-kcal/day deficit diet
- Patients underwent a 4-week dose-escalation period followed by 52 weeks on the full dose
- The primary end points were mean percent weight change, percentage of patients achieving ≥5% of baseline weight loss, and percentage of patients achieving >10% of baseline weight loss at 56 weeks
- Secondary end points included changes in waist circumference, blood pressure, and lipids
- Mean baseline body weight was 233.9 lb and mean BMI was 38.3 kg/m2
- Patients with type 2 diabetes were excluded from participating
Study 1 (3 year)1,2
- Results from a 160-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of Saxenda®
- Adult patients with pre-diabetes and with a BMI of either ≥30 kg/m2, or ≥27 with at least 1 additional comorbidity, were randomized to receive once-daily Saxenda® (n=1,505) or placebo (n=749) in conjunction with a lifestyle modification program that included increased physical activity and a 500-kcal/day-deficit diet
- Patients underwent a 4-week dose escalation period followed by 156 weeks on the full dose, with a 12-week off-drug observational follow-up period
- The study evaluated percentage of patients achieving weight loss of at least 5% of body weight at both 1 year and 3 years
- Mean baseline body weight was 236.7 lb and mean BMI was 38.8 kg/m2
Study 21,4
- Results from a 56-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Saxenda®
- Adult patients with type 2 diabetes with a BMI ≥27 (n=635) were randomized to receive once-daily Saxenda® (n=423) or placebo (n=212), in conjunction with a lifestyle modification program that included increased physical activity and a 500-kcal/day-deficit diet
- Patients were randomized, then underwent a 4-week dose-escalation period followed by 52 weeks on the full dose
- The primary end points were mean percent weight change, percentage of patients achieving ≥5% of baseline weight loss, and percentage of patients achieving >10% of baseline weight loss at 56 weeks
- Mean baseline body weight was 233.0 lb and mean BMI was 37.1 kg/m2
- Patients were to have an A1C of 7% to 10% and be treated with metformin, a sulfonylurea, or a glitazone as a single agent or in any combination, or with diet and exercise alone
Study 31,5
- Results from a 56-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Saxenda®
- Adult patients with a BMI ≥30, or ≥27 with 1 or more weight-related comorbidities (n=422) were randomized to receive once-daily Saxenda® (n=212) or placebo (n=210) in conjunction with a lifestyle modification program that included increased physical activity and a 500-kcal/day-deficit diet
- Patients were first treated with a low-calorie diet (total energy intake: 1,200-1,400 kcal/day) and with increased physical activity in the run-in period lasting up to 12 weeks. Patients who lost at least 5% of screening body weight during the run-in period were randomized, then underwent a 4-week dose-escalation period followed by 52 weeks on the full dose
- The primary end points were mean percent weight change from randomization to week 56, percentage of patients not gaining more than 0.5% body weight from randomization to week 56, and percentage of patients achieving ≥5% weight loss from randomization to week 56
- Mean baseline body weight was 219.1 lb and mean BMI was 35.6 kg/m2
- Patients with type 2 diabetes were excluded from participating
RECOMMENDED CONTENT
Sustained Weight Loss
Important Safety Information for Saxenda®
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
Liraglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures in both genders of rats and mice. It is unknown whether Saxenda® causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans, as the human relevance of liraglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined.
Saxenda® is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC and in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Counsel patients regarding the potential risk of MTC with use of Saxenda® and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (eg, a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with Saxenda®.
Contraindications
Saxenda® is contraindicated in:
- Patients with a personal or family history of MTC or patients with MEN 2
- Patients with a serious hypersensitivity reaction to liraglutide or to any of the excipients in Saxenda®. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported with Saxenda®
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors: If serum calcitonin is measured and found to be elevated, the patient should be further evaluated. Patients with thyroid nodules noted on physical examination or neck imaging should also be further evaluated
- Acute Pancreatitis: Acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, has been observed in patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, including liraglutide. Observe patients carefully for signs and symptoms of acute pancreatitis, which may include persistent or severe abdominal pain (sometimes radiating to the back), nausea or vomiting. If pancreatitis is suspected, discontinue Saxenda® and initiate appropriate management
- Acute Gallbladder Disease: Substantial or rapid weight loss can increase the risk of cholelithiasis; however, the incidence of acute gallbladder disease was greater in patients treated with Saxenda® than with placebo even after accounting for the degree of weight loss. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies and appropriate clinical follow-up are indicated
- Hypoglycemia: Adult patients with type 2 diabetes on an insulin secretagogue (eg, a sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia with use of Saxenda®. The risk may be lowered by a reduction in the dose of insulin secretagogues or insulin. In pediatric patients without type 2 diabetes, hypoglycemia occurred. Inform all patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms
- Heart Rate Increase: Mean increases in resting heart rate of 2 to 3 beats per minute (bpm) were observed in patients treated with Saxenda®. Monitor heart rate at regular intervals and inform patients to report palpitations or feelings of a racing heartbeat while at rest during treatment with Saxenda®. Discontinue Saxenda® in patients who experience a sustained increase in resting heart rate
- Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion: There have been postmarketing reports of acute kidney injury which may sometimes require hemodialysis, in patients treated with liraglutide. The majority of the reported events occurred in patients who had experienced gastrointestinal reactions leading to dehydration such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Monitor renal function in patients reporting adverse reactions to Saxenda® that could lead to volume depletion, especially during initation and escalation of Saxenda®
- Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: Use of Saxenda® has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions, sometimes severe. In clinical trials, severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported more frequently among patients receiving Saxenda® (4.8%) than placebo (1.4%). Saxenda® is not recommended in patients with severe gastroparesis
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (eg, anaphylaxis and angioedema) have been reported in patients treated with Saxenda®. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, patients should stop taking Saxenda® and promptly seek medical advice
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: In adult clinical trials, 9 (0.3%) of 3,384 patients treated with Saxenda® and 2 (0.1%) of the 1,941 treated with placebo reported suicidal ideation; one of the Saxenda® treated patients attempted suicide. In a pediatric trial, 1(0.8%) of the 125 Saxenda® treated patients died by suicide. There was insufficient information to establish a causal relationship to Saxenda®. Monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Discontinue treatment if patients experience suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Avoid Saxenda® in patients with a history of suicidal attempts or active suicidal ideation
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation: Saxenda® delays gastric emptying. There have been rare postmarketing reports of pulmonary aspiration in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation who had residual gastric contents despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers prior to any planned surgeries or procedures if they are taking Saxenda®
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions, reported in ≥5% are nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, injection site reactions, headache, hypoglycemia, dyspepsia, fatigue, dizziness, abdominal pain, increased lipase, upper abdominal pain, pyrexia, and gastroenteritis
Drug Interactions
- Saxenda® causes a delay of gastric emptying and has the potential to impact the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Monitor for potential consequences of delayed absorption of oral medications concomitantly administered with Saxenda®
Use in Specific Populations
- Saxenda® should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- There are no data on the presence of liraglutide in human breast milk; liraglutide was present in the milk of lactating rats
- Saxenda® has not been studied in patients less than 12 years of age
Please click here for Saxenda® Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning.
Indications and Usage
Saxenda® (liraglutide) injection 3 mg is indicated in combination with reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in:
- Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with body weight greater than 60kg and obesity
- Adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight related comorbid condition
Limitations of Use
- Saxenda® contains liraglutide and should not be coadministered with other liraglutide-containing products or with any other GLP-1 receptor agonist
- The safety and effectiveness of Saxenda® in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes have not been established
Important Safety Information for Saxenda®
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
Liraglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures in both genders of rats and mice. It is unknown whether Saxenda® causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans, as the human relevance of liraglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined.
Saxenda® is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC and in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Counsel patients regarding the potential risk of MTC with use of Saxenda® and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (eg, a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with Saxenda®.
Important Safety Information for Saxenda®
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
Liraglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures in both genders of rats and mice. It is unknown whether Saxenda® causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans, as the human relevance of liraglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined.
Saxenda® is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC and in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Counsel patients regarding the potential risk of MTC with use of Saxenda® and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (eg, a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with Saxenda®.
Contraindications
Saxenda® is contraindicated in:
- Patients with a personal or family history of MTC or patients with MEN 2
- Patients with a serious hypersensitivity reaction to liraglutide or to any of the excipients in Saxenda®. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported with Saxenda®
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors: If serum calcitonin is measured and found to be elevated, the patient should be further evaluated. Patients with thyroid nodules noted on physical examination or neck imaging should also be further evaluated
- Acute Pancreatitis: Acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, has been observed in patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, including liraglutide. Observe patients carefully for signs and symptoms of acute pancreatitis, which may include persistent or severe abdominal pain (sometimes radiating to the back), nausea or vomiting. If pancreatitis is suspected, discontinue Saxenda® and initiate appropriate management
- Acute Gallbladder Disease: Substantial or rapid weight loss can increase the risk of cholelithiasis; however, the incidence of acute gallbladder disease was greater in patients treated with Saxenda® than with placebo even after accounting for the degree of weight loss. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies and appropriate clinical follow-up are indicated
- Hypoglycemia: Adult patients with type 2 diabetes on an insulin secretagogue (eg, a sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia with use of Saxenda®. The risk may be lowered by a reduction in the dose of insulin secretagogues or insulin. In pediatric patients without type 2 diabetes, hypoglycemia occurred. Inform all patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms
- Heart Rate Increase: Mean increases in resting heart rate of 2 to 3 beats per minute (bpm) were observed in patients treated with Saxenda®. Monitor heart rate at regular intervals and inform patients to report palpitations or feelings of a racing heartbeat while at rest during treatment with Saxenda®. Discontinue Saxenda® in patients who experience a sustained increase in resting heart rate
- Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion: There have been postmarketing reports of acute kidney injury which may sometimes require hemodialysis, in patients treated with liraglutide. The majority of the reported events occurred in patients who had experienced gastrointestinal reactions leading to dehydration such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Monitor renal function in patients reporting adverse reactions to Saxenda® that could lead to volume depletion, especially during initation and escalation of Saxenda®
- Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: Use of Saxenda® has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions, sometimes severe. In clinical trials, severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported more frequently among patients receiving Saxenda® (4.8%) than placebo (1.4%). Saxenda® is not recommended in patients with severe gastroparesis
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (eg, anaphylaxis and angioedema) have been reported in patients treated with Saxenda®. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, patients should stop taking Saxenda® and promptly seek medical advice
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: In adult clinical trials, 9 (0.3%) of 3,384 patients treated with Saxenda® and 2 (0.1%) of the 1,941 treated with placebo reported suicidal ideation; one of the Saxenda® treated patients attempted suicide. In a pediatric trial, 1(0.8%) of the 125 Saxenda® treated patients died by suicide. There was insufficient information to establish a causal relationship to Saxenda®. Monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Discontinue treatment if patients experience suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Avoid Saxenda® in patients with a history of suicidal attempts or active suicidal ideation
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation: Saxenda® delays gastric emptying. There have been rare postmarketing reports of pulmonary aspiration in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation who had residual gastric contents despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers prior to any planned surgeries or procedures if they are taking Saxenda®
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions, reported in ≥5% are nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, injection site reactions, headache, hypoglycemia, dyspepsia, fatigue, dizziness, abdominal pain, increased lipase, upper abdominal pain, pyrexia, and gastroenteritis
Drug Interactions
- Saxenda® causes a delay of gastric emptying and has the potential to impact the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Monitor for potential consequences of delayed absorption of oral medications concomitantly administered with Saxenda®
Use in Specific Populations
- Saxenda® should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- There are no data on the presence of liraglutide in human breast milk; liraglutide was present in the milk of lactating rats
- Saxenda® has not been studied in patients less than 12 years of age
Please click here for Saxenda® Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning.
Indications and Usage
Saxenda® (liraglutide) injection 3 mg is indicated in combination with reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in:
- Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with body weight greater than 60kg and obesity
- Adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight related comorbid condition
Limitations of Use
- Saxenda® contains liraglutide and should not be coadministered with other liraglutide-containing products or with any other GLP-1 receptor agonist
- The safety and effectiveness of Saxenda® in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes have not been established
References
1. Saxenda® [package insert]. Plainsboro, NJ: Novo Nordisk Inc.
2. le Roux CW, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. 3 years of liraglutide versus placebo for type 2 diabetes risk reduction and weight management in individuals with prediabetes: a randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10077):1399-1409.
3. Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):11-22.
4. Davies MJ, Bergenstal R, Bode B, et al; for NN8022-1922 Study Group. Efficacy of liraglutide for weight loss among patients with type 2 diabetes: the SCALE Diabetes randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314(7):687-699.
5. Wadden TA, Hollander P, Klein S, et al; for NN8022-1923 Investigators. Weight maintenance and additional weight loss with liraglutide after low-calorie-diet-induced weight loss: the SCALE Maintenance randomized study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2013;37(11):1443-1451.