EASY TO USEa BASED ON THE FLEXPRO® YOU KNOW1
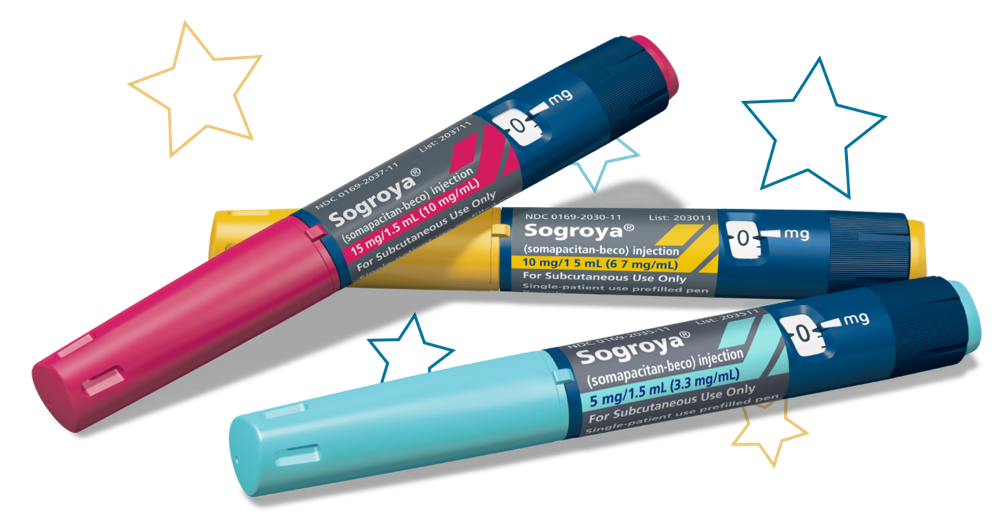

No mixing required
Prefilled, premixed, and preloaded.2
Portable
Stable at room temperature (up to 77 °F) for up to 3 days (72 hours).2,b
Precise dosing
Over 150 dosing increments available across all pens2
aBased on a randomized, crossover device preference and handling study of the Sogroya® pen in 33 adolescents aged 10 to 17 years with growth-related disorders and 37 caregivers ≥18 years of age. After training, users performed simulated injections into a pad or mannequin and then completed the DHPAQ. 99% (69) of participants found the Sogroya® pen easy or very easy to use.1
bThe pen should be refrigerated (36 °F-46 °F). If needed, it may be stored at room temperature (up to 77 °F) for no more than 72 hours total. The pen can be taken in and out of a refrigerator as needed. The pen must be discarded 6 weeks after first use, if it has been frozen or if kept above 86 °F. See Prescribing Information for full storage and handling instructions.2
Sogroya® is indicated for pediatric patients aged 2.5 years and older with growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (GH), and for replacement of endogenous GH in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD). Please see full indications.
EASY TO USEa BASED ON THE FLEXPRO® YOU KNOW1
No mixing required
Prefilled, premixed, and preloaded.2
Portable
Stable at room temperature (up to 77 °F) for up to 3 days (72 hours).2,b
Precise dosing
Over 150 dosing increments available across all pens2
aBased on a randomized, crossover device preference and handling study of the Sogroya® pen in 33 adolescents aged 10 to 17 years with growth-related disorders and 37 caregivers ≥18 years of age. After training, users performed simulated injections into a pad or mannequin and then completed the DHPAQ. 99% (69) of participants found the Sogroya® pen easy or very easy to use.1
bThe pen should be refrigerated (36 °F-46 °F). If needed, it may be stored at room temperature (up to 77 °F) for no more than 72 hours total. The pen can be taken in and out of a refrigerator as needed. The pen must be discarded 6 weeks after first use, if it has been frozen or if kept above 86 °F. See Prescribing Information for full storage and handling instructions.2
Most patients and caregivers preferred the Sogroya® pen over Skytrofa® auto-injector and Ngenla® pen1,3,c
Results from a randomized, crossover study assessing device preference and ease of use following simulated injections with the Sogroya® pen and Skytrofa® auto-injector or Ngenla® pen.
preferred the Sogroya® pen over Skytrofa® auto-injector3,c
(14% preferred Skytrofa® auto-injector; 7% had no preference between devices)
Sogroya® pen was easy or very easy to use3,c
(57% considered Skytrofa® auto-injector easy or very easy to use)
preferred Sogroya® pen over Ngenla® pen1,c
(13% preferred Ngenla® pen; 3% had no preference between devices)
Sogroya® pen was easy or very easy to use1,c
(74% considered Ngenla® pen easy or very easy to use)
preferred the Sogroya® pen over Skytrofa® auto-injector3,c
(14% preferred Skytrofa® auto-injector; 7% had no preference between devices)
Sogroya® pen was easy or very easy to use3,c
(57% considered Skytrofa® auto-injector easy or very easy to use)

preferred Sogroya® pen over Ngenla® pen1,c
(13% preferred Ngenla® pen; 3% had no preference between devices)
Sogroya® pen was easy or very easy to use1,c
(74% considered Ngenla® pen easy or very easy to use)

Results based on two open-label, multicenter, randomized, crossover studies of the same design. One study compared the handling of Sogroya® pen vs Ngenla® pen in 70 participants, naïve to both or similar devices: 33 adolescents with growth-related disorders aged 10 to 17 years, and 37 caregivers ≥18 years of age. The other study compared the handling of Sogroya® pen vs Skytrofa® auto-injector in 70 participants, naïve to both or similar devices: 35 adolescents with growth-related disorders aged 10 to 17 years, and 35 caregivers ≥18 years of age. The primary objective of both studies was to evaluate patient device preference as measured by the Device Handling and Preference Assessment Questionnaire (DHPAQ). Another objective was to compare the ease of use of the 2 devices included in the study. Other endpoints included device training time, preparation and injection time, and overall number of complete injections. After receiving training for both devices included in the study, participants performed a simulated injection into a pad or mannequin and completed the DHPAQ. Confirmatory validation of the DHPAQ was done via postinjection cognitive interviews, confirming that the DHPAQ was comprehensive, relevant to their experiences, and fully comprehended by the participants.1,3
Limitations: A US-only, small sample size participant pool of 2 distinct groups, potentially reducing statistical power. Adolescents were not required to be injection naïve and children under 10 years were excluded. Assessment of treatment adherence or adverse events was not done. The studies took place in a controlled setting with assessment at a single time point, not reflecting long-term use.
cThese data do not establish clinical comparability of the products for any indications and should not be seen as making any claim regarding efficacy and safety. These data make no representation or conclusion as to the factors contributing to patient preference. All percentages have been rounded to the nearest whole number.
The Sogroya® pen: designed with your patients in mind
Dose counter lets patients view the dose prescribed2
Dose selector allows patients to choose the dose they need2
Dose button for patients to administer medication2
Dose counter lets patients view the dose prescribed2
Dose selector allows patients to choose the dose they need2
Dose button for patients to administer medication2
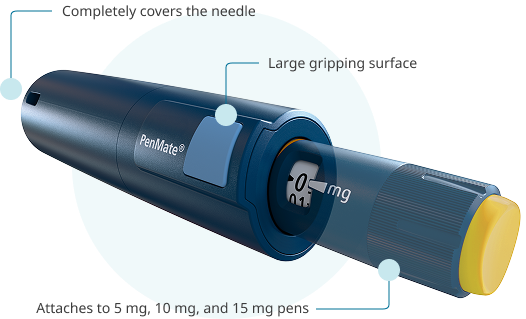
PenMate® keeps needles out of sight
Now approved for Sogroya®, PenMate® is a reusable cover for the 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg pens. Once attached to the end of a pen, it completely covers the needle, keeping it unseen as it enters the skin. PenMate® also has a large gripping surface for holding firmly.
Patients can order their PenMate® by contacting their NovoCare® Case Manager or by calling 1‑888‑668‑6444.
Pediatric dosing
See dosing information for switch and treatment-naïve patients alike.
See dosing information for switch and treatment-naïve patients alike.
Device attribute chart
Learn about select features of the Sogroya® pen and other growth hormone therapy devices.
Learn about select features of the Sogroya® pen and other growth hormone therapy devices.
Important Safety Information for Sogroya®
Contraindications
Sogroya® is contraindicated in patients with:
- acute critical illness after open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, or acute respiratory failure because of the risk of increased mortality with use of Sogroya®
- hypersensitivity to Sogroya® or any of its excipients. Systemic hypersensitivity reactions have been reported postmarketing with somatropin
- pediatric patients with closed epiphyses
- active malignancy
- active proliferative or severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese, have a history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or have severe respiratory impairment due to risk of sudden death
Warnings & Precautions
- Increased Mortality in Patients with Acute Critical Illness: Increased mortality has been reported after treatment with somatropin in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, and in patients with acute respiratory failure
- Severe Hypersensitivity: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported postmarketing with use of somatropin. Inform patients and/or caregivers that such reactions are possible and that prompt medical attention should be sought if an allergic reaction occurs
- Increased Risk of Neoplasms: There is an increased risk of malignancy progression with somatropin in patients with active malignancy. Any preexisting malignancy should be inactive, and its treatment complete prior to instituting Sogroya®. In childhood cancer survivors treated with radiation to the brain/head for their first neoplasm who developed subsequent GHD and were treated with somatropin, an increased risk of a second neoplasm has been reported. Monitor patients with a history of GHD secondary to an intracranial neoplasm for progression or recurrence of the tumor. Children with certain rare genetic causes of short stature have an increased risk of developing malignancies and should be carefully monitored for development of neoplasms. Monitor patients for increased growth or potential malignant changes of preexisting nevi. Advise patients/caregivers to report changes in the appearance of preexisting nevi
- Glucose Intolerance and Diabetes Mellitus: Treatment with somatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. New onset type 2 diabetes has been reported. Monitor glucose levels in all patients, especially in those with existing diabetes mellitus or with risk factors for diabetes mellitus, such as obesity, Turner syndrome, or a family history of diabetes mellitus. The doses of antidiabetic agents may require adjustment when Sogroya® is initiated
- Intracranial Hypertension: Has been reported usually within 8 weeks of treatment initiation. Perform fundoscopic examination prior to initiation of treatment and periodically thereafter. If papilledema is identified, evaluate the etiology and treat the underlying cause before initiating Sogroya®. If papilledema is observed, stop treatment. If intracranial hypertension is confirmed, Sogroya® can be restarted at a lower dose after intracranial hypertension signs and symptoms have resolved
- Fluid Retention: May occur during Sogroya® therapy. Clinical manifestations of fluid retention (e.g. edema and nerve compression syndromes, including carpal tunnel syndrome/paresthesia) are usually transient and dose dependent
- Hypoadrenalism: Patients receiving somatropin therapy who have or are at risk for corticotropin deficiency may be at risk for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or unmasking of central (secondary) hypoadrenalism. Patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®. Monitor patients with known hypoadrenalism for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or need for glucocorticoid dose increases
- Hypothyroidism: Undiagnosed/untreated hypothyroidism may prevent an optimal response to Sogroya®. Monitor thyroid function periodically as hypothyroidism may occur or worsen after initiation of Sogroya®
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Pediatric Patients: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may occur more frequently in patients undergoing rapid growth. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may lead to osteonecrosis. Cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with or without osteonecrosis have been reported in pediatric patients with short stature receiving somatropin. Evaluate pediatric patients receiving Sogroya® with the onset of a limp or complaints of persistent hip or knee pain for slipped capital femoral epiphysis and osteonecrosis and manage accordingly
- Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis in Pediatric Patients: Monitor patients with a history of scoliosis for disease progression
- Pancreatitis: Cases of pancreatitis have been reported in patients receiving somatropin. The risk may be greater in pediatric patients compared to adults. Consider pancreatitis in patients with persistent severe abdominal pain
- Lipohypertrophy/Lipoatrophy: May occur if Sogroya® is administered at the same site over a long period of time. Rotate injection sites to reduce this risk
- Sudden Death in Pediatric Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome: There have been reports of fatalities after initiating therapy with somatropin in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who had one or more of the following risk factors: severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or unidentified respiratory infection. Male patients with one or more of these factors may be at greater risk than females. Sogroya® is not indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to genetically confirmed Prader-Willi syndrome
- Laboratory Tests: Serum levels of inorganic phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase may increase after Sogroya® therapy. Serum levels of parathyroid hormone may increase with somatropin treatment
Adverse Reactions
- Pediatric patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients are nasopharyngitis, headache, pyrexia, pain in extremity, and injection site reaction
- Adult patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in >2% of patients are back pain, arthralgia, dyspepsia, sleep disorder, dizziness, tonsillitis, peripheral edema, vomiting, adrenal insufficiency, hypertension, blood creatine phosphokinase increase, weight increase, and anemia
Drug Interactions
- Glucocorticoids: Patients treated with glucocorticoid for hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®
- Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs: Sogroya® may alter the clearance. Monitor carefully if used with Sogroya®
- Oral Estrogen: Patients receiving oral estrogen replacement may require higher Sogroya® dosages
- Insulin and/or Other Antihyperglycemic Agents: Dose adjustment of insulin and/or antihyperglycemic agent may be required for patients with diabetes mellitus
Please click here for Sogroya® Prescribing Information.
Indications and Usage
Sogroya® (somapacitan-beco) injection 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg is indicated for the:
- treatment of pediatric patients aged 2.5 years and older who have growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (GH)
- replacement of endogenous GH in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD)
Indications and Usage
Sogroya® (somapacitan-beco) injection 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg is indicated for the:
- treatment of pediatric patients aged 2.5 years and older who have growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (GH)
- replacement of endogenous GH in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD)
Important Safety Information for Sogroya®
Contraindications
Sogroya® is contraindicated in patients with:
- acute critical illness after open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, or acute respiratory failure because of the risk of increased mortality with use of Sogroya®
- hypersensitivity to Sogroya® or any of its excipients. Systemic hypersensitivity reactions have been reported postmarketing with somatropin
- pediatric patients with closed epiphyses
- active malignancy
- active proliferative or severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese, have a history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or have severe respiratory impairment due to risk of sudden death
Warnings & Precautions
- Increased Mortality in Patients with Acute Critical Illness: Increased mortality has been reported after treatment with somatropin in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, and in patients with acute respiratory failure
- Severe Hypersensitivity: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported postmarketing with use of somatropin. Inform patients and/or caregivers that such reactions are possible and that prompt medical attention should be sought if an allergic reaction occurs
- Increased Risk of Neoplasms: There is an increased risk of malignancy progression with somatropin in patients with active malignancy. Any preexisting malignancy should be inactive, and its treatment complete prior to instituting Sogroya®. In childhood cancer survivors treated with radiation to the brain/head for their first neoplasm who developed subsequent GHD and were treated with somatropin, an increased risk of a second neoplasm has been reported. Monitor patients with a history of GHD secondary to an intracranial neoplasm for progression or recurrence of the tumor. Children with certain rare genetic causes of short stature have an increased risk of developing malignancies and should be carefully monitored for development of neoplasms. Monitor patients for increased growth or potential malignant changes of preexisting nevi. Advise patients/caregivers to report changes in the appearance of preexisting nevi
- Glucose Intolerance and Diabetes Mellitus: Treatment with somatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. New onset type 2 diabetes has been reported. Monitor glucose levels in all patients, especially in those with existing diabetes mellitus or with risk factors for diabetes mellitus, such as obesity, Turner syndrome, or a family history of diabetes mellitus. The doses of antidiabetic agents may require adjustment when Sogroya® is initiated
- Intracranial Hypertension: Has been reported usually within 8 weeks of treatment initiation. Perform fundoscopic examination prior to initiation of treatment and periodically thereafter. If papilledema is identified, evaluate the etiology and treat the underlying cause before initiating Sogroya®. If papilledema is observed, stop treatment. If intracranial hypertension is confirmed, Sogroya® can be restarted at a lower dose after intracranial hypertension signs and symptoms have resolved
- Fluid Retention: May occur during Sogroya® therapy. Clinical manifestations of fluid retention (e.g. edema and nerve compression syndromes, including carpal tunnel syndrome/paresthesia) are usually transient and dose dependent
- Hypoadrenalism: Patients receiving somatropin therapy who have or are at risk for corticotropin deficiency may be at risk for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or unmasking of central (secondary) hypoadrenalism. Patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®. Monitor patients with known hypoadrenalism for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or need for glucocorticoid dose increases
- Hypothyroidism: Undiagnosed/untreated hypothyroidism may prevent an optimal response to Sogroya®. Monitor thyroid function periodically as hypothyroidism may occur or worsen after initiation of Sogroya®
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Pediatric Patients: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may occur more frequently in patients undergoing rapid growth. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may lead to osteonecrosis. Cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with or without osteonecrosis have been reported in pediatric patients with short stature receiving somatropin. Evaluate pediatric patients receiving Sogroya® with the onset of a limp or complaints of persistent hip or knee pain for slipped capital femoral epiphysis and osteonecrosis and manage accordingly
- Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis in Pediatric Patients: Monitor patients with a history of scoliosis for disease progression
- Pancreatitis: Cases of pancreatitis have been reported in patients receiving somatropin. The risk may be greater in pediatric patients compared to adults. Consider pancreatitis in patients with persistent severe abdominal pain
- Lipohypertrophy/Lipoatrophy: May occur if Sogroya® is administered at the same site over a long period of time. Rotate injection sites to reduce this risk
- Sudden Death in Pediatric Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome: There have been reports of fatalities after initiating therapy with somatropin in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who had one or more of the following risk factors: severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or unidentified respiratory infection. Male patients with one or more of these factors may be at greater risk than females. Sogroya® is not indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to genetically confirmed Prader-Willi syndrome
- Laboratory Tests: Serum levels of inorganic phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase may increase after Sogroya® therapy. Serum levels of parathyroid hormone may increase with somatropin treatment
Adverse Reactions
- Pediatric patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients are nasopharyngitis, headache, pyrexia, pain in extremity, and injection site reaction
- Adult patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in >2% of patients are back pain, arthralgia, dyspepsia, sleep disorder, dizziness, tonsillitis, peripheral edema, vomiting, adrenal insufficiency, hypertension, blood creatine phosphokinase increase, weight increase, and anemia
Drug Interactions
- Glucocorticoids: Patients treated with glucocorticoid for hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®
- Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs: Sogroya® may alter the clearance. Monitor carefully if used with Sogroya®
- Oral Estrogen: Patients receiving oral estrogen replacement may require higher Sogroya® dosages
- Insulin and/or Other Antihyperglycemic Agents: Dose adjustment of insulin and/or antihyperglycemic agent may be required for patients with diabetes mellitus
Please click here for Sogroya® Prescribing Information.
Indications and Usage
Sogroya® (somapacitan-beco) injection 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg is indicated for the:
- treatment of pediatric patients aged 2.5 years and older who have growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (GH)
- replacement of endogenous GH in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD)
Important Safety Information for Sogroya®
Contraindications
Sogroya® is contraindicated in patients with:
- acute critical illness after open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, or acute respiratory failure because of the risk of increased mortality with use of Sogroya®
- hypersensitivity to Sogroya® or any of its excipients. Systemic hypersensitivity reactions have been reported postmarketing with somatropin
- pediatric patients with closed epiphyses
- active malignancy
- active proliferative or severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese, have a history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or have severe respiratory impairment due to risk of sudden death
Important Safety Information for Sogroya®
Contraindications
Sogroya® is contraindicated in patients with:
- acute critical illness after open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, or acute respiratory failure because of the risk of increased mortality with use of Sogroya®
- hypersensitivity to Sogroya® or any of its excipients. Systemic hypersensitivity reactions have been reported postmarketing with somatropin
- pediatric patients with closed epiphyses
- active malignancy
- active proliferative or severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese, have a history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or have severe respiratory impairment due to risk of sudden death
Warnings & Precautions
- Increased Mortality in Patients with Acute Critical Illness: Increased mortality has been reported after treatment with somatropin in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, and in patients with acute respiratory failure
- Severe Hypersensitivity: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported postmarketing with use of somatropin. Inform patients and/or caregivers that such reactions are possible and that prompt medical attention should be sought if an allergic reaction occurs
- Increased Risk of Neoplasms: There is an increased risk of malignancy progression with somatropin in patients with active malignancy. Any preexisting malignancy should be inactive, and its treatment complete prior to instituting Sogroya®. In childhood cancer survivors treated with radiation to the brain/head for their first neoplasm who developed subsequent GHD and were treated with somatropin, an increased risk of a second neoplasm has been reported. Monitor patients with a history of GHD secondary to an intracranial neoplasm for progression or recurrence of the tumor. Children with certain rare genetic causes of short stature have an increased risk of developing malignancies and should be carefully monitored for development of neoplasms. Monitor patients for increased growth or potential malignant changes of preexisting nevi. Advise patients/caregivers to report changes in the appearance of preexisting nevi
- Glucose Intolerance and Diabetes Mellitus: Treatment with somatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. New onset type 2 diabetes has been reported. Monitor glucose levels in all patients, especially in those with existing diabetes mellitus or with risk factors for diabetes mellitus, such as obesity, Turner syndrome, or a family history of diabetes mellitus. The doses of antidiabetic agents may require adjustment when Sogroya® is initiated
- Intracranial Hypertension: Has been reported usually within 8 weeks of treatment initiation. Perform fundoscopic examination prior to initiation of treatment and periodically thereafter. If papilledema is identified, evaluate the etiology and treat the underlying cause before initiating Sogroya®. If papilledema is observed, stop treatment. If intracranial hypertension is confirmed, Sogroya® can be restarted at a lower dose after intracranial hypertension signs and symptoms have resolved
- Fluid Retention: May occur during Sogroya® therapy. Clinical manifestations of fluid retention (e.g. edema and nerve compression syndromes, including carpal tunnel syndrome/paresthesia) are usually transient and dose dependent
- Hypoadrenalism: Patients receiving somatropin therapy who have or are at risk for corticotropin deficiency may be at risk for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or unmasking of central (secondary) hypoadrenalism. Patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®. Monitor patients with known hypoadrenalism for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or need for glucocorticoid dose increases
- Hypothyroidism: Undiagnosed/untreated hypothyroidism may prevent an optimal response to Sogroya®. Monitor thyroid function periodically as hypothyroidism may occur or worsen after initiation of Sogroya®
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Pediatric Patients: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may occur more frequently in patients undergoing rapid growth. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may lead to osteonecrosis. Cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with or without osteonecrosis have been reported in pediatric patients with short stature receiving somatropin. Evaluate pediatric patients receiving Sogroya® with the onset of a limp or complaints of persistent hip or knee pain for slipped capital femoral epiphysis and osteonecrosis and manage accordingly
- Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis in Pediatric Patients: Monitor patients with a history of scoliosis for disease progression
- Pancreatitis: Cases of pancreatitis have been reported in patients receiving somatropin. The risk may be greater in pediatric patients compared to adults. Consider pancreatitis in patients with persistent severe abdominal pain
- Lipohypertrophy/Lipoatrophy: May occur if Sogroya® is administered at the same site over a long period of time. Rotate injection sites to reduce this risk
- Sudden Death in Pediatric Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome: There have been reports of fatalities after initiating therapy with somatropin in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who had one or more of the following risk factors: severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or unidentified respiratory infection. Male patients with one or more of these factors may be at greater risk than females. Sogroya® is not indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to genetically confirmed Prader-Willi syndrome
- Laboratory Tests: Serum levels of inorganic phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase may increase after Sogroya® therapy. Serum levels of parathyroid hormone may increase with somatropin treatment
Adverse Reactions
- Pediatric patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients are nasopharyngitis, headache, pyrexia, pain in extremity, and injection site reaction
- Adult patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in >2% of patients are back pain, arthralgia, dyspepsia, sleep disorder, dizziness, tonsillitis, peripheral edema, vomiting, adrenal insufficiency, hypertension, blood creatine phosphokinase increase, weight increase, and anemia
Drug Interactions
- Glucocorticoids: Patients treated with glucocorticoid for hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®
- Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs: Sogroya® may alter the clearance. Monitor carefully if used with Sogroya®
- Oral Estrogen: Patients receiving oral estrogen replacement may require higher Sogroya® dosages
- Insulin and/or Other Antihyperglycemic Agents: Dose adjustment of insulin and/or antihyperglycemic agent may be required for patients with diabetes mellitus
Please click here for Sogroya® Prescribing Information.
Important Safety Information for Sogroya®
Contraindications
Sogroya® is contraindicated in patients with:
- acute critical illness after open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, or acute respiratory failure because of the risk of increased mortality with use of Sogroya®
- hypersensitivity to Sogroya® or any of its excipients. Systemic hypersensitivity reactions have been reported postmarketing with somatropin
- pediatric patients with closed epiphyses
- active malignancy
- active proliferative or severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese, have a history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or have severe respiratory impairment due to risk of sudden death
Warnings & Precautions
- Increased Mortality in Patients with Acute Critical Illness: Increased mortality has been reported after treatment with somatropin in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, and in patients with acute respiratory failure
- Severe Hypersensitivity: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported postmarketing with use of somatropin. Inform patients and/or caregivers that such reactions are possible and that prompt medical attention should be sought if an allergic reaction occurs
- Increased Risk of Neoplasms: There is an increased risk of malignancy progression with somatropin in patients with active malignancy. Any preexisting malignancy should be inactive, and its treatment complete prior to instituting Sogroya®. In childhood cancer survivors treated with radiation to the brain/head for their first neoplasm who developed subsequent GHD and were treated with somatropin, an increased risk of a second neoplasm has been reported. Monitor patients with a history of GHD secondary to an intracranial neoplasm for progression or recurrence of the tumor. Children with certain rare genetic causes of short stature have an increased risk of developing malignancies and should be carefully monitored for development of neoplasms. Monitor patients for increased growth or potential malignant changes of preexisting nevi. Advise patients/caregivers to report changes in the appearance of preexisting nevi
- Glucose Intolerance and Diabetes Mellitus: Treatment with somatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. New onset type 2 diabetes has been reported. Monitor glucose levels in all patients, especially in those with existing diabetes mellitus or with risk factors for diabetes mellitus, such as obesity, Turner syndrome, or a family history of diabetes mellitus. The doses of antidiabetic agents may require adjustment when Sogroya® is initiated
- Intracranial Hypertension: Has been reported usually within 8 weeks of treatment initiation. Perform fundoscopic examination prior to initiation of treatment and periodically thereafter. If papilledema is identified, evaluate the etiology and treat the underlying cause before initiating Sogroya®. If papilledema is observed, stop treatment. If intracranial hypertension is confirmed, Sogroya® can be restarted at a lower dose after intracranial hypertension signs and symptoms have resolved
- Fluid Retention: May occur during Sogroya® therapy. Clinical manifestations of fluid retention (e.g. edema and nerve compression syndromes, including carpal tunnel syndrome/paresthesia) are usually transient and dose dependent
- Hypoadrenalism: Patients receiving somatropin therapy who have or are at risk for corticotropin deficiency may be at risk for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or unmasking of central (secondary) hypoadrenalism. Patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®. Monitor patients with known hypoadrenalism for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or need for glucocorticoid dose increases
- Hypothyroidism: Undiagnosed/untreated hypothyroidism may prevent an optimal response to Sogroya®. Monitor thyroid function periodically as hypothyroidism may occur or worsen after initiation of Sogroya®
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Pediatric Patients: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may occur more frequently in patients undergoing rapid growth. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may lead to osteonecrosis. Cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with or without osteonecrosis have been reported in pediatric patients with short stature receiving somatropin. Evaluate pediatric patients receiving Sogroya® with the onset of a limp or complaints of persistent hip or knee pain for slipped capital femoral epiphysis and osteonecrosis and manage accordingly
- Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis in Pediatric Patients: Monitor patients with a history of scoliosis for disease progression
- Pancreatitis: Cases of pancreatitis have been reported in patients receiving somatropin. The risk may be greater in pediatric patients compared to adults. Consider pancreatitis in patients with persistent severe abdominal pain
- Lipohypertrophy/Lipoatrophy: May occur if Sogroya® is administered at the same site over a long period of time. Rotate injection sites to reduce this risk
- Sudden Death in Pediatric Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome: There have been reports of fatalities after initiating therapy with somatropin in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who had one or more of the following risk factors: severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or unidentified respiratory infection. Male patients with one or more of these factors may be at greater risk than females. Sogroya® is not indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to genetically confirmed Prader-Willi syndrome
- Laboratory Tests: Serum levels of inorganic phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase may increase after Sogroya® therapy. Serum levels of parathyroid hormone may increase with somatropin treatment
Adverse Reactions
- Pediatric patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients are nasopharyngitis, headache, pyrexia, pain in extremity, and injection site reaction
- Adult patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in >2% of patients are back pain, arthralgia, dyspepsia, sleep disorder, dizziness, tonsillitis, peripheral edema, vomiting, adrenal insufficiency, hypertension, blood creatine phosphokinase increase, weight increase, and anemia
Drug Interactions
- Glucocorticoids: Patients treated with glucocorticoid for hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®
- Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs: Sogroya® may alter the clearance. Monitor carefully if used with Sogroya®
- Oral Estrogen: Patients receiving oral estrogen replacement may require higher Sogroya® dosages
- Insulin and/or Other Antihyperglycemic Agents: Dose adjustment of insulin and/or antihyperglycemic agent may be required for patients with diabetes mellitus
Please click here for Sogroya® Prescribing Information.
Indications and Usage
Sogroya® (somapacitan-beco) injection 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg is indicated for the:
- treatment of pediatric patients aged 2.5 years and older who have growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (GH)
- replacement of endogenous GH in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD)
Indications and Usage
Sogroya® (somapacitan-beco) injection 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg is indicated for the:
- treatment of pediatric patients aged 2.5 years and older who have growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (GH)
- replacement of endogenous GH in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD)
Important Safety Information for Sogroya®
Contraindications
Sogroya® is contraindicated in patients with:
- acute critical illness after open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, or acute respiratory failure because of the risk of increased mortality with use of Sogroya®
- hypersensitivity to Sogroya® or any of its excipients. Systemic hypersensitivity reactions have been reported postmarketing with somatropin
- pediatric patients with closed epiphyses
- active malignancy
- active proliferative or severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese, have a history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or have severe respiratory impairment due to risk of sudden death
Warnings & Precautions
- Increased Mortality in Patients with Acute Critical Illness: Increased mortality has been reported after treatment with somatropin in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open-heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, and in patients with acute respiratory failure
- Severe Hypersensitivity: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported postmarketing with use of somatropin. Inform patients and/or caregivers that such reactions are possible and that prompt medical attention should be sought if an allergic reaction occurs
- Increased Risk of Neoplasms: There is an increased risk of malignancy progression with somatropin in patients with active malignancy. Any preexisting malignancy should be inactive, and its treatment complete prior to instituting Sogroya®. In childhood cancer survivors treated with radiation to the brain/head for their first neoplasm who developed subsequent GHD and were treated with somatropin, an increased risk of a second neoplasm has been reported. Monitor patients with a history of GHD secondary to an intracranial neoplasm for progression or recurrence of the tumor. Children with certain rare genetic causes of short stature have an increased risk of developing malignancies and should be carefully monitored for development of neoplasms. Monitor patients for increased growth or potential malignant changes of preexisting nevi. Advise patients/caregivers to report changes in the appearance of preexisting nevi
- Glucose Intolerance and Diabetes Mellitus: Treatment with somatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. New onset type 2 diabetes has been reported. Monitor glucose levels in all patients, especially in those with existing diabetes mellitus or with risk factors for diabetes mellitus, such as obesity, Turner syndrome, or a family history of diabetes mellitus. The doses of antidiabetic agents may require adjustment when Sogroya® is initiated
- Intracranial Hypertension: Has been reported usually within 8 weeks of treatment initiation. Perform fundoscopic examination prior to initiation of treatment and periodically thereafter. If papilledema is identified, evaluate the etiology and treat the underlying cause before initiating Sogroya®. If papilledema is observed, stop treatment. If intracranial hypertension is confirmed, Sogroya® can be restarted at a lower dose after intracranial hypertension signs and symptoms have resolved
- Fluid Retention: May occur during Sogroya® therapy. Clinical manifestations of fluid retention (e.g. edema and nerve compression syndromes, including carpal tunnel syndrome/paresthesia) are usually transient and dose dependent
- Hypoadrenalism: Patients receiving somatropin therapy who have or are at risk for corticotropin deficiency may be at risk for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or unmasking of central (secondary) hypoadrenalism. Patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®. Monitor patients with known hypoadrenalism for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or need for glucocorticoid dose increases
- Hypothyroidism: Undiagnosed/untreated hypothyroidism may prevent an optimal response to Sogroya®. Monitor thyroid function periodically as hypothyroidism may occur or worsen after initiation of Sogroya®
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Pediatric Patients: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may occur more frequently in patients undergoing rapid growth. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may lead to osteonecrosis. Cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with or without osteonecrosis have been reported in pediatric patients with short stature receiving somatropin. Evaluate pediatric patients receiving Sogroya® with the onset of a limp or complaints of persistent hip or knee pain for slipped capital femoral epiphysis and osteonecrosis and manage accordingly
- Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis in Pediatric Patients: Monitor patients with a history of scoliosis for disease progression
- Pancreatitis: Cases of pancreatitis have been reported in patients receiving somatropin. The risk may be greater in pediatric patients compared to adults. Consider pancreatitis in patients with persistent severe abdominal pain
- Lipohypertrophy/Lipoatrophy: May occur if Sogroya® is administered at the same site over a long period of time. Rotate injection sites to reduce this risk
- Sudden Death in Pediatric Patients with Prader-Willi Syndrome: There have been reports of fatalities after initiating therapy with somatropin in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who had one or more of the following risk factors: severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or unidentified respiratory infection. Male patients with one or more of these factors may be at greater risk than females. Sogroya® is not indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to genetically confirmed Prader-Willi syndrome
- Laboratory Tests: Serum levels of inorganic phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase may increase after Sogroya® therapy. Serum levels of parathyroid hormone may increase with somatropin treatment
Adverse Reactions
- Pediatric patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients are nasopharyngitis, headache, pyrexia, pain in extremity, and injection site reaction
- Adult patients with GHD: Adverse reactions reported in >2% of patients are back pain, arthralgia, dyspepsia, sleep disorder, dizziness, tonsillitis, peripheral edema, vomiting, adrenal insufficiency, hypertension, blood creatine phosphokinase increase, weight increase, and anemia
Drug Interactions
- Glucocorticoids: Patients treated with glucocorticoid for hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of Sogroya®
- Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs: Sogroya® may alter the clearance. Monitor carefully if used with Sogroya®
- Oral Estrogen: Patients receiving oral estrogen replacement may require higher Sogroya® dosages
- Insulin and/or Other Antihyperglycemic Agents: Dose adjustment of insulin and/or antihyperglycemic agent may be required for patients with diabetes mellitus
Please click here for Sogroya® Prescribing Information.
References:
- Akhtar S, Berg B, Medina J, et al. Patients with growth-related disorders and caregivers prefer the somapacitan device to the somatrogon device: results from a randomized crossover study assessing device preference and ease of use following simulated injections. Med Devices (Auckl). 2024;17:427-439.
- Sogroya [package insert]. Plainsboro, NJ: Novo Nordisk Inc.
- Medina J, Ter-Borch G, Kelepouris N, et al. Usability and preference evaluation of the somapacitan pen-injector and lonapegsomatropin autoinjector: results of a US-based simulated-use study with adolescent patients and caregivers. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2025;19:1119-1131. doi:10.2147/PPA.S505952