Vagifem® (estradiol vaginal inserts) is an estrogen indicated for the treatment of atrophic vaginitis due to menopause.
The therapeutic goal should be to use the most appropriate, often lowest, effective dose of systemic estrogen therapy consistent with treatment goals.1
Dosing
Patients should take Vagifem® 10 mcg in a two-step dosing regimen.2
Patients should take Vagifem® 10 mcg in a two-step dosing regimen.2
- Initial dose: one tablet inserted intravaginally once daily for two weeks
- Continued dose: one tablet inserted intravaginally twice weekly—for example, Tuesday and Friday
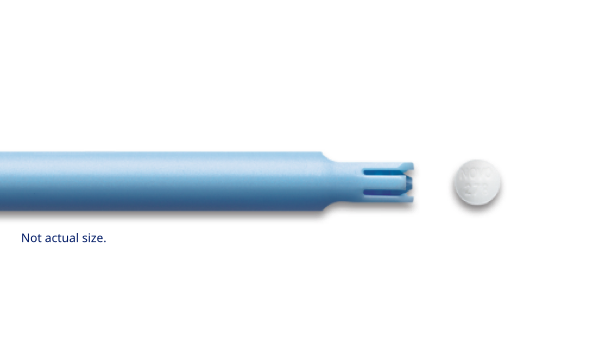
Preloaded applicators2
Preloaded applicators2
The preloaded, single-use Vagifem® 10 mcg applicators come individually packaged in a blister pack and should be discarded after each use.2
The preloaded, single-use Vagifem® 10 mcg applicators come individually packaged in a blister pack and should be discarded after each use.2
Important Safety Information for Vagifem®
WARNING: ENDOMETRIAL CANCER, CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS, PROBABLE DEMENTIA, and BREAST CANCER
Estrogen-Alone Therapy
Endometrial Cancer
There is an increased risk of endometrial cancer in a woman with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens. Adding a progestogen to estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Perform adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding.
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen-alone substudy reported increased risks of stroke and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 7.1 years of treatment with daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) [0.625 mg]-alone, relative to placebo.
The WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older during 5.2 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone, relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women.
Do not use estrogen-alone therapy for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Only daily oral 0.625 mg CE was studied in the estrogen-alone substudy of the WHI. Therefore, the relevance of the WHI findings regarding adverse cardiovascular events and dementia to lower CE doses, other routes of administration, or other estrogen-alone products is not known. Without such data, it is not possible to definitively exclude these risks or determine the extent of these risks for other products. Discuss with your patient the benefits and risks of estrogen-alone therapy, taking into account her individual risk profile.
Prescribe estrogens with or without progestogens at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Estrogen Plus Progestin Therapy
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy reported increased risks of pulmonary embolism (PE), DVT, stroke, and myocardial infarction (MI) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 5.6 years of treatment with daily oral CE (0.625 mg) combined with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) [2.5 mg], relative to placebo.
The WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study of the WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older during 4 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) combined with MPA (2.5 mg), relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women.
Do not use estrogen plus progestogen therapy for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Breast Cancer
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy demonstrated an increased risk of invasive breast cancer.
Only daily oral 0.625 mg CE and 2.5 mg MPA were studied in the estrogen plus progestin substudy of the WHI. Therefore, the relevance of the WHI findings regarding adverse cardiovascular events, dementia and breast cancer to lower CE plus other MPA doses, other routes of administration, or other estrogen plus progestogen products is not known. Without such data, it is not possible to definitively exclude these risks or determine the extent of these risks for other products. Discuss with your patient the benefits and risks of estrogen plus progestogen therapy, taking into account her individual risk profile.
Prescribe estrogens with or without progestogens at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Contraindications
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
- Breast cancer or a history of breast cancer
- Estrogen-dependent neoplasia
- Active DVT, PE, or history of these conditions
- Active arterial thromboembolic disease (for example, stroke or MI), or a history of these conditions
- Known anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, or hypersensitivity to Vagifem®
- Hepatic impairment or disease
- Protein C, protein S, or antithrombin deficiency, or other known thrombophilic disorders
Warnings and Precautions
- Risks from systemic absorption: Vagifem® is intended only for vaginal administration. Systemic absorption occurs with the use of Vagifem®. The warnings, precautions, and adverse reactions associated with the use of systemic estrogen-alone therapy should be taken into account.
- Cardiovascular Disorders: Immediately discontinue estrogen with or without progestogen therapy if PE, DVT, stroke, or MI occur or are suspected.
- Malignant Neoplasms: Extension of the WHI trials also demonstrated increased breast cancer risk associated with systemic estrogen plus progestin therapy. One large meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies reported increased risks that were dependent upon duration of use of systemic estrogen plus progestin therapy and systemic estrogen-alone therapy. These risks could last up to >10 years after discontinuation of these systemic therapies depending on the duration of use. There was no increase in risk of developing breast cancer in women taking vaginal estrogens. The CE plus MPA substudy of WHI reported a statistically non-significant increased risk of ovarian cancer with the use of estrogen plus progestin. A meta-analysis of 17 prospective and 35 retrospective studies found that women who used hormonal therapy for menopausal symptoms had an increased risk for ovarian cancer.
- Gallbladder disease: A 2-4-fold increase in the risk of gallbladder disease requiring surgery in postmenopausal women receiving estrogens has been reported.
- Discontinue Vagifem® if severe hypercalcemia, visual abnormalities (sudden loss of vision, sudden onset of proptosis, diplopia, or migraine), severe hypertriglyceridemia, cholestatic jaundice or medically concerning fluid retention occurs.
- Exacerbation of Hypothyroidism: Monitor thyroid function in women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy who are also receiving estrogens because estrogen leads to increased thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) levels.
- Local abrasion: A few cases of local abrasion induced by the Vagifem® applicator have been reported.
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5 percent) with Vagifem® are back pain, vulvovaginal pruritus, vulvovaginal mycotic infection, and diarrhea.
Drug Interactions
- Inducers and inhibitors of CYP3A4 may affect estrogen drug metabolism and decrease or increase the estrogen plasma concentration.
Please click here for Vagifem® Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning.
Important Safety Information for Vagifem®
WARNING: ENDOMETRIAL CANCER, CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS, PROBABLE DEMENTIA, and BREAST CANCER
Estrogen-Alone Therapy
Endometrial Cancer
There is an increased risk of endometrial cancer in a woman with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens. Adding a progestogen to estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Perform adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding.
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen-alone substudy reported increased risks of stroke and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 7.1 years of treatment with daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) [0.625 mg]-alone, relative to placebo.
The WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older during 5.2 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone, relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women.
Do not use estrogen-alone therapy for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Only daily oral 0.625 mg CE was studied in the estrogen-alone substudy of the WHI. Therefore, the relevance of the WHI findings regarding adverse cardiovascular events and dementia to lower CE doses, other routes of administration, or other estrogen-alone products is not known. Without such data, it is not possible to definitively exclude these risks or determine the extent of these risks for other products. Discuss with your patient the benefits and risks of estrogen-alone therapy, taking into account her individual risk profile.
Prescribe estrogens with or without progestogens at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Estrogen Plus Progestin Therapy
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy reported increased risks of pulmonary embolism (PE), DVT, stroke, and myocardial infarction (MI) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 5.6 years of treatment with daily oral CE (0.625 mg) combined with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) [2.5 mg], relative to placebo.
The WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study of the WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older during 4 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) combined with MPA (2.5 mg), relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women.
Do not use estrogen plus progestogen therapy for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Breast Cancer
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy demonstrated an increased risk of invasive breast cancer.
Only daily oral 0.625 mg CE and 2.5 mg MPA were studied in the estrogen plus progestin substudy of the WHI. Therefore, the relevance of the WHI findings regarding adverse cardiovascular events, dementia and breast cancer to lower CE plus other MPA doses, other routes of administration, or other estrogen plus progestogen products is not known. Without such data, it is not possible to definitively exclude these risks or determine the extent of these risks for other products. Discuss with your patient the benefits and risks of estrogen plus progestogen therapy, taking into account her individual risk profile.
Prescribe estrogens with or without progestogens at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Important Safety Information for Vagifem®
WARNING: ENDOMETRIAL CANCER, CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS, PROBABLE DEMENTIA, and BREAST CANCER
Estrogen-Alone Therapy
Endometrial Cancer
There is an increased risk of endometrial cancer in a woman with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens. Adding a progestogen to estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Perform adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding.
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen-alone substudy reported increased risks of stroke and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 7.1 years of treatment with daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) [0.625 mg]-alone, relative to placebo.
The WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older during 5.2 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone, relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women.
Do not use estrogen-alone therapy for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Only daily oral 0.625 mg CE was studied in the estrogen-alone substudy of the WHI. Therefore, the relevance of the WHI findings regarding adverse cardiovascular events and dementia to lower CE doses, other routes of administration, or other estrogen-alone products is not known. Without such data, it is not possible to definitively exclude these risks or determine the extent of these risks for other products. Discuss with your patient the benefits and risks of estrogen-alone therapy, taking into account her individual risk profile.
Prescribe estrogens with or without progestogens at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Estrogen Plus Progestin Therapy
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy reported increased risks of pulmonary embolism (PE), DVT, stroke, and myocardial infarction (MI) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 5.6 years of treatment with daily oral CE (0.625 mg) combined with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) [2.5 mg], relative to placebo.
The WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study of the WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older during 4 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) combined with MPA (2.5 mg), relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women.
Do not use estrogen plus progestogen therapy for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Breast Cancer
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy demonstrated an increased risk of invasive breast cancer.
Only daily oral 0.625 mg CE and 2.5 mg MPA were studied in the estrogen plus progestin substudy of the WHI. Therefore, the relevance of the WHI findings regarding adverse cardiovascular events, dementia and breast cancer to lower CE plus other MPA doses, other routes of administration, or other estrogen plus progestogen products is not known. Without such data, it is not possible to definitively exclude these risks or determine the extent of these risks for other products. Discuss with your patient the benefits and risks of estrogen plus progestogen therapy, taking into account her individual risk profile.
Prescribe estrogens with or without progestogens at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Contraindications
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
- Breast cancer or a history of breast cancer
- Estrogen-dependent neoplasia
- Active DVT, PE, or history of these conditions
- Active arterial thromboembolic disease (for example, stroke or MI), or a history of these conditions
- Known anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, or hypersensitivity to Vagifem®
- Hepatic impairment or disease
- Protein C, protein S, or antithrombin deficiency, or other known thrombophilic disorders
Warnings and Precautions
- Risks from systemic absorption: Vagifem® is intended only for vaginal administration. Systemic absorption occurs with the use of Vagifem®. The warnings, precautions, and adverse reactions associated with the use of systemic estrogen-alone therapy should be taken into account.
- Cardiovascular Disorders: Immediately discontinue estrogen with or without progestogen therapy if PE, DVT, stroke, or MI occur or are suspected.
- Malignant Neoplasms: Extension of the WHI trials also demonstrated increased breast cancer risk associated with systemic estrogen plus progestin therapy. One large meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies reported increased risks that were dependent upon duration of use of systemic estrogen plus progestin therapy and systemic estrogen-alone therapy. These risks could last up to >10 years after discontinuation of these systemic therapies depending on the duration of use. There was no increase in risk of developing breast cancer in women taking vaginal estrogens. The CE plus MPA substudy of WHI reported a statistically non-significant increased risk of ovarian cancer with the use of estrogen plus progestin. A meta-analysis of 17 prospective and 35 retrospective studies found that women who used hormonal therapy for menopausal symptoms had an increased risk for ovarian cancer.
- Gallbladder disease: A 2-4-fold increase in the risk of gallbladder disease requiring surgery in postmenopausal women receiving estrogens has been reported.
- Discontinue Vagifem® if severe hypercalcemia, visual abnormalities (sudden loss of vision, sudden onset of proptosis, diplopia, or migraine), severe hypertriglyceridemia, cholestatic jaundice or medically concerning fluid retention occurs.
- Exacerbation of Hypothyroidism: Monitor thyroid function in women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy who are also receiving estrogens because estrogen leads to increased thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) levels.
- Local abrasion: A few cases of local abrasion induced by the Vagifem® applicator have been reported.
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5 percent) with Vagifem® are back pain, vulvovaginal pruritus, vulvovaginal mycotic infection, and diarrhea.
Drug Interactions
- Inducers and inhibitors of CYP3A4 may affect estrogen drug metabolism and decrease or increase the estrogen plasma concentration.
Please click here for Vagifem® Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning.
References
- North American Menopause Society. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause: The Journal of the North American Menopause Society. 2017;24(7):728-753.
- Vagifem [package insert]. Princeton, NJ Novo Nordisk FemCare AG.