Clinical education library
Browse our library of clinical education, offering insights into diabetes pathophysiology and treatment, practice management, and patient care. All are ready to watch, download, or share with your colleagues.
Filter

education
AACE Guidelines
See guidance on screening and diagnosis criteria, and approaches for treating patients with diabetes.

website
Diabetes Risk Assessment Tool
Estimate your patient’s 5-year and 10-year potential risk of diabetes-related health complications.

Exploring a Population Health Management (PHM) Approach: A Health System Perspective
In part 3 of 5, Dr. Bradley Eilerman discusses the steps to PHM implementation and its value.

education
Insurance coverage
Easily verify coverage, estimate costs, and submit prior authorizations with NovoCare®.

Exploring a Population Health Management (PHM) Approach: Approach of an ACO
In part 5 of 5, Dr Michael Sobolero shares how PHM has impacted diabetes management in his practice.

education
ADA Standards of Care
Full and abridged versions of the standards published by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) are now available.
11:27
Beta-Cell Dysfunction: A Driver of T2D?
Primary care experts discuss beta-cell function in T2D, its role in disease, how it’s measured, and what it means for future research.
15:29
The Role of Endogenous GLP-1
Experts review the history of GLP-1 discovery and explain how endogenous GLP-1 influences type 2 diabetes pathophysiology and treatment.
9:15
Understanding the Role of Insufficient GLP-1 Activity in T2D
Experts review GLP-1’s role in glucose regulation, effects on beta cells, and options to address insufficient GLP-1 activity in T2D.
15:39
T2D and Cardiovascular Disease
Join the conversation with experts Dr John Anderson (PCP), Dr Pam Taub (cardiologist), and Dr Mark Greathouse (cardiologist).

TIR HCP Educational Content: Patient Video Lasse
Video about Lasse, a patient with type 1 diabetes, explaining his experience with using Time in range.

TIR HCP Educational Content: What is Time in Range - Animated Explainer Video
Animation to explain what Time in Range is.
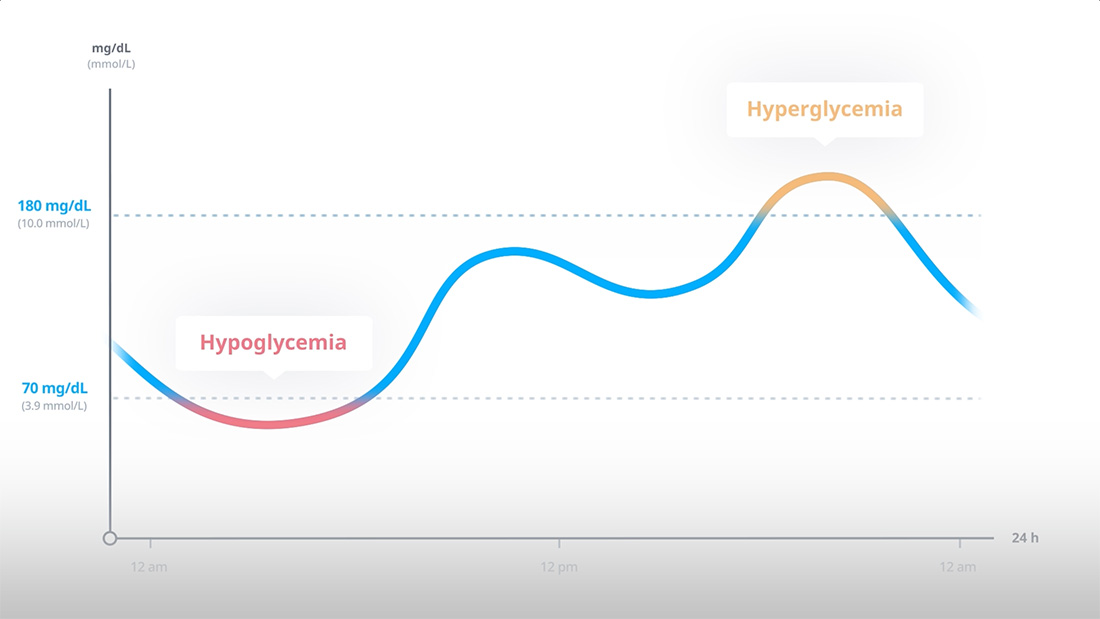
TIR HCP Educational Content: HbA1c and Time in Range - Animated Explainer Video
A video to explain why Time in Range matters and how it correlates to A1c.

TIR HCP Educational Content: Time in Range KOL Video of Dr Cheng
Interview with KOL Alice Cheng on Time in Range.

TIR HCP Educational Content: Time in Range KOL Video of Dr Bergenstal
Interview with Richard Bergenstal on Time in Range and the Ambulatory Glucose Profile.

The Indispensable Role of Pharmacists in T2D Care
Podcast featuring pharmacy experts on why pharmacists are vital in T2D care, including data, outcomes, and treatment recommendations.