WHAT IS TIME IN RANGE (TIR)?
TIR is a metric that expresses the percentage of time a person with diabetes spends within their target glucose range.1 TIR is measured by continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and may be used with other CGM metrics, including Time Below Range (TBR), Time Above Range (TAR), mean glucose, and glycemic variability, to assess a person’s glucose levels.1,2

TIR, a clinical metric for assessing glycemic control1
The American Diabetes Association Standards of Care and the International Consensus Report on Time in Range (TIR) recommend that many nonpregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes spend at least 70% of the day (around 17 hours) in the target glycemic range of 70 to 180 mg/dL, which corresponds to the recommended hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) target of approximately 7%.1,2

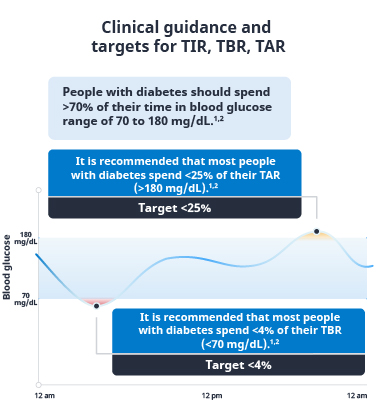
For patients who are pregnant, older, or are at high risk, please see recommendations here.
HOW TIR WORKS WITH HBA1C
TIR is a complement to HbA1c, the current gold standard for assessing glucose control.1-4 For more than 3 decades, HbA1c has been relied on as both a diagnostic measure and diabetes management tool for people with diabetes and healthcare professionals.4 However, while HbA1c measures a person’s average blood glucose levels over the previous 2 to 3 months, it does not provide a measure of daily fluctuations.1,2 Moreover, it does not capture the daily variable occurrence of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.1,2 In fact, 2 people with the same HbA1c results could have very different daily glucose profiles.5
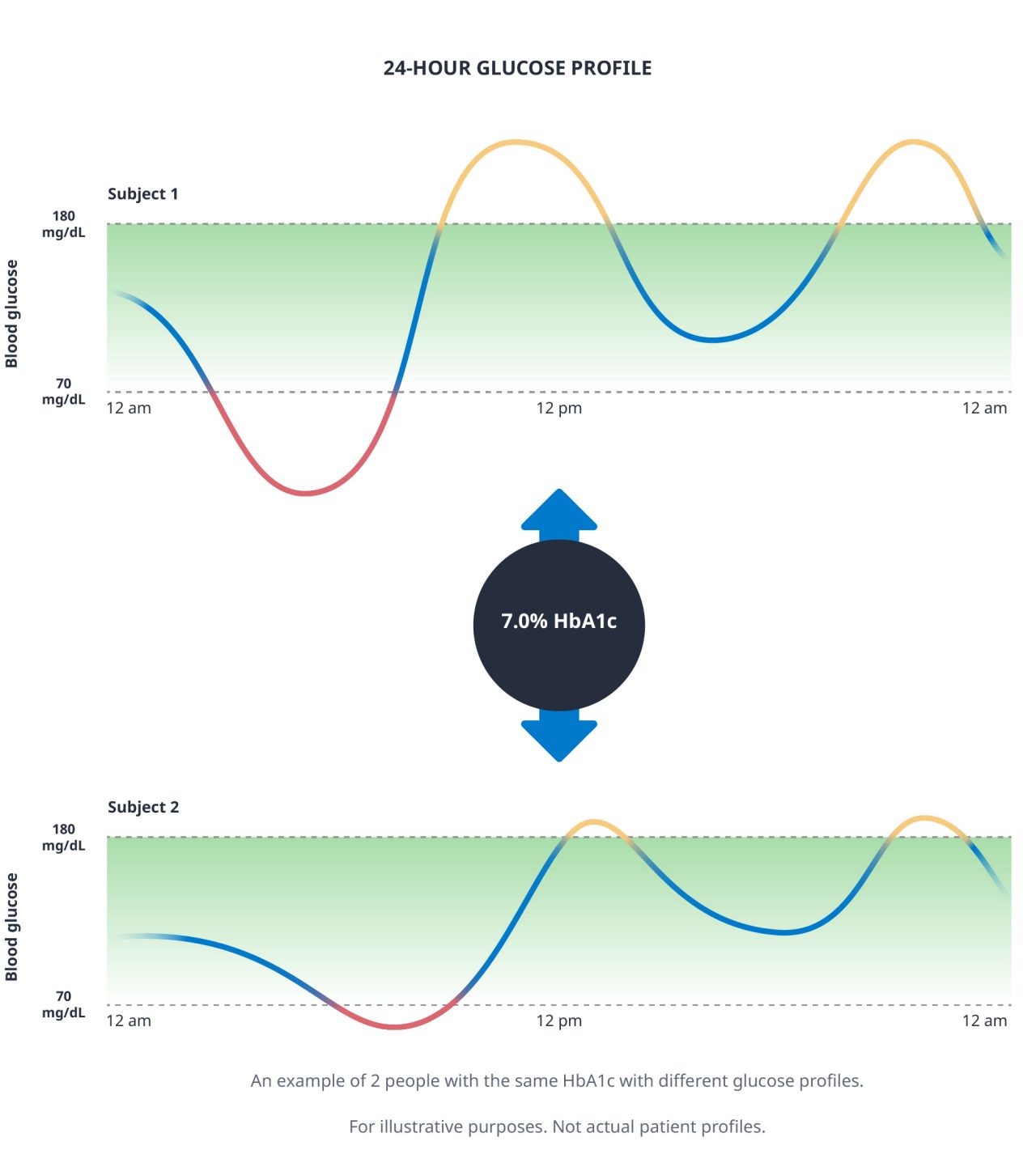
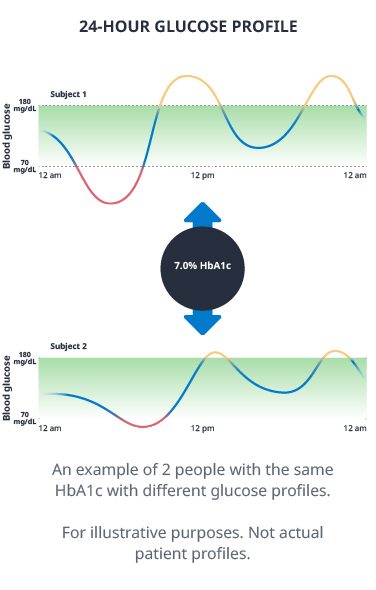
TIR, together with TBR and TAR, may offer a more complementary picture of glucose levels and has the potential to reveal fluctuations in glucose levels throughout the day. When used in conjunction with HbA1c, TIR can tell a personalized, individual story about glucose levels, helping people with diabetes to understand both their daily fluctuations and what may be driving them, and helping healthcare professionals make more informed decisions in managing diabetes.1,2
- Battelino T, Danne T, Bergenstal RM, et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(8):1593-1603.
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(suppl 1):S1-S291.
- Danne T, Nimri R, Battelino T, et al. International Consensus on Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(12):1631-1640.
- Chehregosha H, Khamseh ME, Malek M, et al. A View Beyond HbA1C: Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Ther. 2019;10(3):853-863.
- Dunn TC, Hayter GA, Doniger KJ, et al. Development of the Likelihood of Low Glucose (LLG) algorithm for evaluating risk of hypoglycemia: a new approach for using continuous glucose data to guide therapeutic decision making. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2014;8(4):720-730.